Research paper added to the NSS Space Solar Power Library: Opportunities and Challenges for Space Solar for Remote Installations, Naval Research Laboratory, October 2019.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Energy is critical for essentially every human activity. A practical capability to send energy to a range of sites directly from space to augment or supplant traditional military energy supply lines presents compelling benefits. As the Department of Defense’s energy requirements evolve, pursuit of existing and prospective energy options has yet to illuminate a path toward a long-term, resilient, and logistically tenable solution.
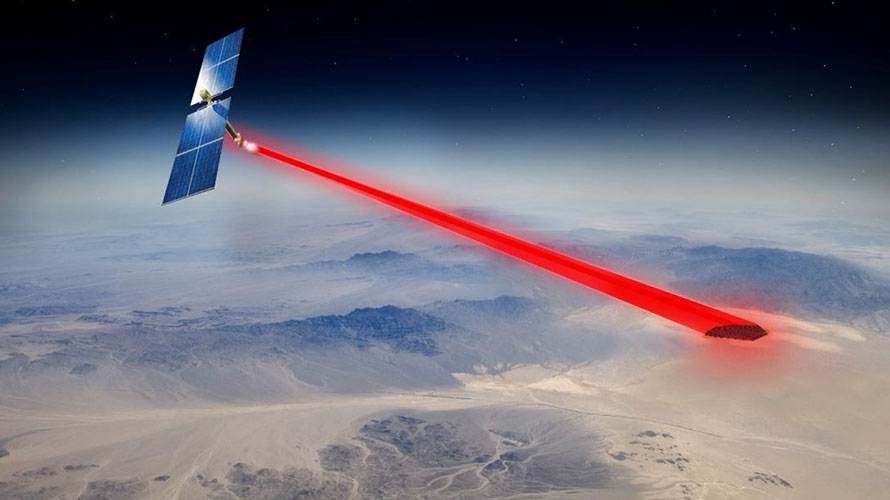
Power beaming technology forms the foundation of a possible solution. Space solar would depend intrinsically on this technology. With space solar, unfiltered, continuous sunlight is collected and converted by satellites in space and sent to points of need on Earth. This approach unlocks novel operating scenarios and capabilities for military and space operations. Key advances in spacecraft mass-production, power conversion, lightweight materials, commercial reusable launch, and space robotics within recent years have led subject matter experts to suggest that renewed in-depth investigation of these possibilities is warranted.
This study report extends previous efforts in order to clarify the time frame of potential feasibility and identify prospective means of providing power to military and remote installations via space solar. The goal of the study was to determine the feasibility of a coordinated development effort for a military and remote installation energy resupply capability via space solar. This report includes key findings of opportunities and challenges, as well as recommendations for advancing the development of technologies applicable to space solar for remote installations.
The study team determined that there remain significant unresolved technological, economic, legal/political, operational/organizational, and schedule challenges inherent in the development of a deployable space solar capability. Important questions regarding the most promising approaches and prospective utility for operationally relevant contexts have yet to be definitively answered because of technological immaturity and uncertainties in non-technical areas. In light of these challenges and questions, paired with the potential game-changing nature of space solar, now is the time for the Department of Defense to lead measured investment by Operational Energy stakeholders in these six key areas: (1) Space Solar Collection, (2) Power Beaming Transmission, (3) Power Beaming Reception, (4) Receiver Power Distribution, (5) Architecture Analytics, and (6) Supporting Technologies. Technology gaps identified during the course of the study appear in Appendix A, and the development plans formulated are captured in Appendix B.
Efforts in these six areas will directly support the execution of integrated demonstrations of progressively increasing capability, which in turn will give insight into applicability to emerging paradigms, such as battlefield electrification and the shift towards autonomous systems. The likely economic viability of space solar for military energy supply as compared to alternatives should be reassessed regularly by tracking progress and trends of these four metrics: space transportation cost, space hardware cost, specific power of the space segment, and the contribution of costs from the receiver segment. In parallel, the legal/political roadblocks should be addressed, particularly for spectrum and orbit allocations. Likewise, it is critical to monitor and at minimum maintain parity with foreign developments. Operational utility should be further discerned and informed via modeling and analysis efforts. Together, these will shed light on the schedule horizon and appropriate further steps forward.



















1 thought on “Opportunities and Challenges for Space Solar for Remote Installations”
Here is a rough draft for a SSPS suporting “Spin-Hab” Short Radius Human Centrifuge which is workable for the middle ear…17 RPM 4 Meter Radius will not incapacitate passengers or crew…;-) https://www.facebook.com/geoff.s.jones/posts/10214015507957867